Clinical trials are designed to determine if a new drug or treatment will work on a disease or will potentially be of benefit to patients. Throughout this guide, we will explore how do clinical trials work; clinical trials’ complexities, answer key questions, provide data-driven insights, and examine their profound impact on healthcare.
To streamline all your Clinical Trials, we have Kerlo Sense, that makes your user experience super friendly and lets you cater and manage all your clinical trials and studies requirements at one place.
What are the 3 types of Clinical Trials?
Below-mentioned are 3 types of Clinical trials, that is subdivided into more funnel; for further information, you can deep dive in types of Clinical Trials:
Treatment Trials: In these trials, new treatments are compared to dummy treatments or standard therapies in order to determine their effectiveness.
Prevention Trials: These trials aim to reduce the risk of developing a specific disease by testing vaccines or medications.
Diagnostic Trials: Such studies examine new methods of detecting and diagnosing diseases, including imaging and tests.
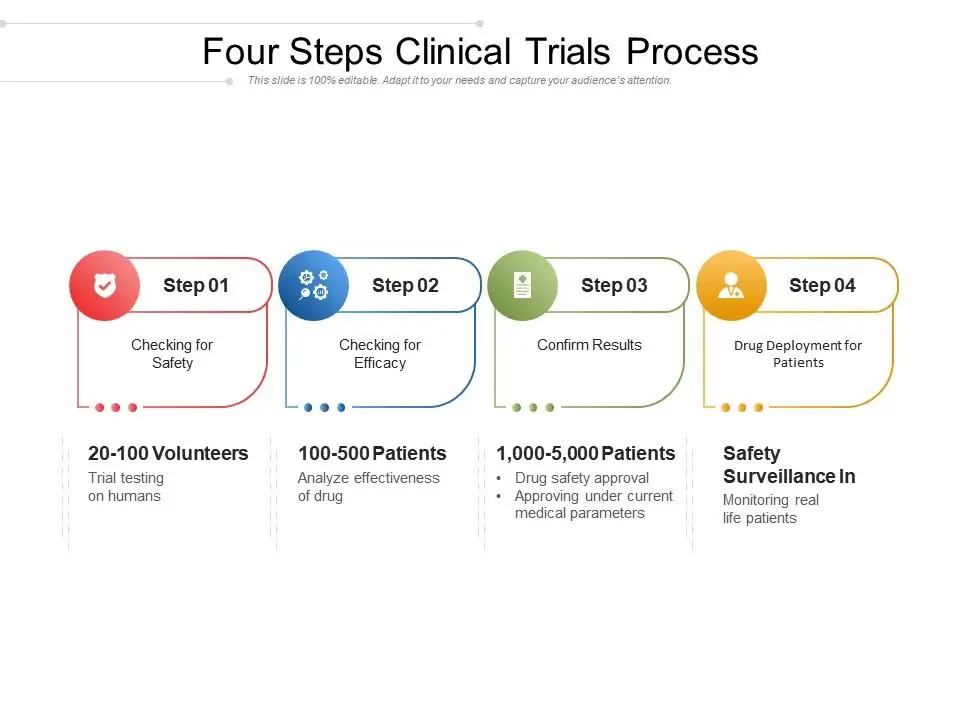
What are the 4 phases of Clinical Trials?
Below are the 4 phases through which a Clinical trial goes through:
Phase I Clinical Trial
The purpose of Phase 1 is to ensure that the treatment is safe in humans and to determine how and where it distributes within the body.
Phase II Clinical Trial
The purpose of a Phase 2 Clinical Trial is to determine the right dosage and effectiveness in treating that particular disease.
Phase III Clinical Trial
The purpose of Phase 3 is confirming the treatment’s effectiveness, monitoring side effects, and comparing it to existing treatments or placebos. This involves a large and diverse population, often spanning multiple locations.
Phase IV Clinical Trial
Phase IV Clinical Trial is responsible for post-marketing surveillance through which they continuously monitor the treatment after it has been approved and made available to the public.
What Are the Benefits of Clinical Trials?
Mostly, people ask “is it safe to participate in clinical trials?” Definitely, it includes some risks but benefits outweigh them. Here are a few benefits of conducting Clinical trials that we can count on fingertips:
- Get paid.
- You get to know more about your disease or health condition.
- Get proper treatment for a particular disease for free.
- Gain access to new and possibly effective treatments or medicine available only to those participating in the trial.
- Have the chance to help society and other people with your disease or health condition by contributing to medical research
Questions to Ask Before Participating in Clinical Research
Carefully conducted clinical trials are performed in human volunteers to provide answers to questions such as:
- Does a treatment work?
- Does it work better than other treatments?
- Does it have side effects?
How Do Researchers Decide Who Will Participate?
Each study has its own set of evaluation criteria to check who can participate. This depends on the research question being asked and may include:
- Age
- Behavior
- Health status
- Additional traits
Frequently Asked Questions
What are clinical trials?
Clinical trials are research investigations in which people are subjected to a medicinal, surgical, or behavioral treatment to see how they affect human health outcomes.
What is clinical research?
Clinical research is the study of people’s health and sickness. It is the method by which we learn to avoid, diagnose, and cure sickness.
Is it safe to participate in clinical trials?
There are some risks associated with clinical trials and studies. It is possible, for example, for certain physical tests to increase the chance of falling, and X-rays to increase the risk of developing minor cancer.
Can I get paid for participating in a Clinical Trial?
Yes, you definitely get paid for participating in a Clinical trial, and the average hourly pay for a Clinical Trials in the United States is $62.52 an hour.
Who conducts clinical trials?
Every clinical trial is led by the principal investigator, who is frequently a physician. A research team for clinical studies may comprise doctors, nurses, social workers, and other health care experts.
How long do clinical trials take?
Usually, the length of study for phase 3 clinical trials is usually 1 to 4 years, but this time span varies. There are many factors that affect how long it takes for a drug to be licensed depending on the phases of clinical trials, just like phase 1 takes 0-1 year, and phase 2 and 3 might take 3-4 years.
Why are clinical trials important?
Clinical trials are important for identifying innovative treatments for diseases as well as new methods for detecting, diagnosing, and reducing the risk of getting the disease.
Who is not eligible for clinical trials?
There is a list of characteristics that excludes a person from participating, and that may vary from demographic information like age, gender, or race to something as complex as comorbidities, organ dysfunction, or the use of other medications.
What is the difference between a clinical trial and a clinical study?
Clinical trials are interventional studies that involve testing medicinal products, while clinical studies might comprise both interventional and non-interventional investigations but do not involve investigational medicinal goods.
Wrapping It Up:
Once you reach this point of the blog post, we assure you that now you have enough knowledge about what clinical trials are and why they are important. By understanding Clinical trial’s intricacies and potential, individuals can make informed decisions about participating, contributing to the collective effort to enhance healthcare for all.

